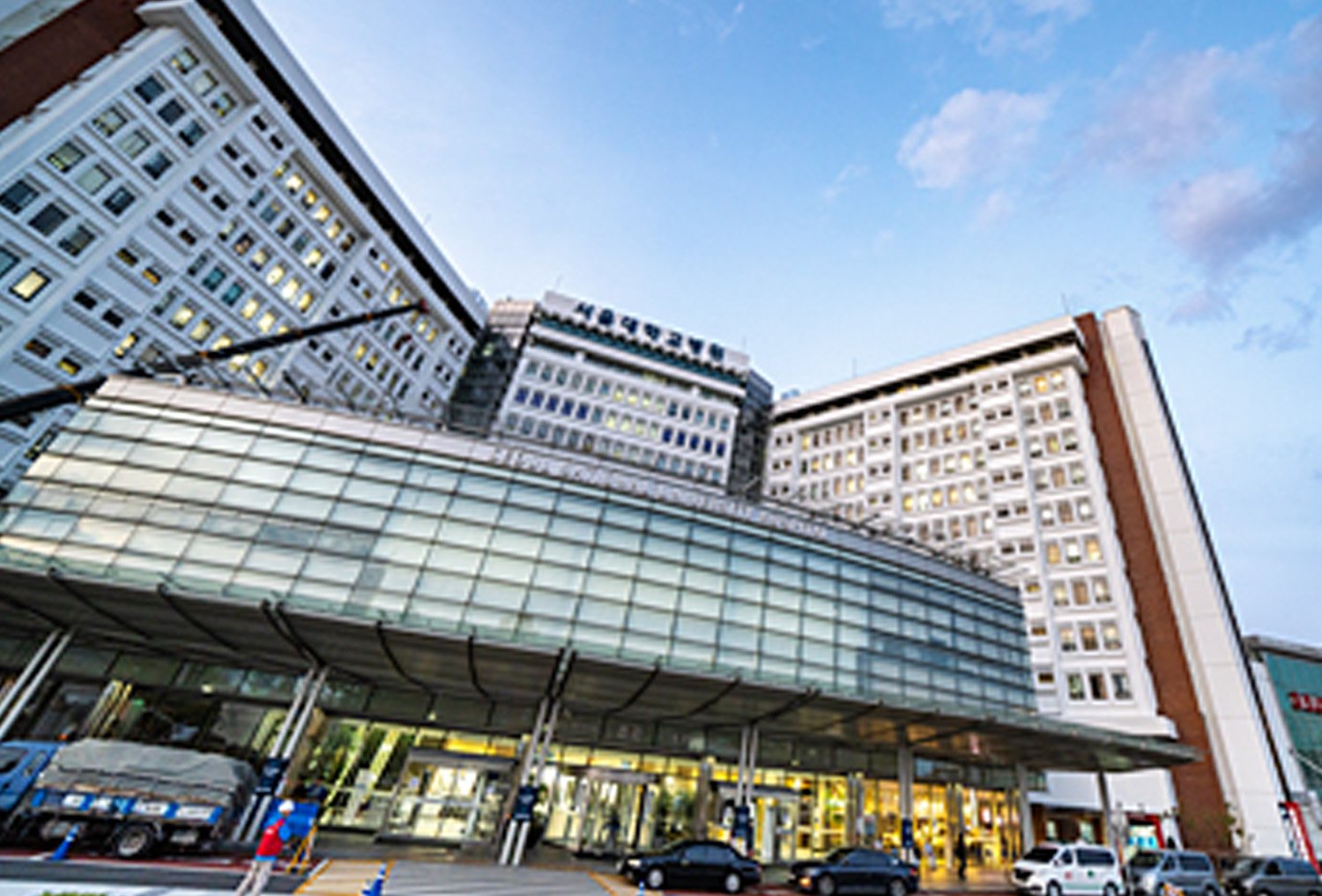
Overall, the health status of the Korean population is better than that of several other Asian countries. The Republic has achieved universal health coverage. Public healthcare is not free, but it is reasonable. Although the country faced one of the world’s largest initial Covid-19 outbreaks outside China, it managed to contain the virus quickly, without imposing a nationwide lockdown.
From 1960 to 1990, the infant mortality rate plummeted, from 80 deaths per 1,000 births to just 13, and average life expectancy at birth increased from 55 to 72 years. As per capita GDP grew – from US$158 in 1960 to US$6,610 in 1990 to US$12,257 in 2000, the ability of workers and companies to pay into a compulsory health insurance system, introduced in 1977, also improved. The pillars of the South Korean model are universal health coverage, equitable access, and cost-effectiveness. On average, residents only need to cover 20 per cent of their medical treatments. If you are employed, five per cent of your income will go towards the NHI. South Korea provides national health insurance to all citizens through the National Health Insurance Corporation.
Be the first to write a comment.